Website malware is malicious software that is specifically designed to compromise the security of a website or web server. This can take many forms, including viruses, worms, Trojans, and other types of malware.
Website malware can have serious consequences, including data theft, identity theft, and the disruption of website operations. It is important for website owners and operators to take steps to protect their sites from malware, such as keeping their software and servers up to date, using strong passwords, and implementing security measures like firewalls and antivirus software.
How does malware enter a website?
There are several ways that malware can enter a website, including:
- Through vulnerable software: Websites that use outdated or unpatched software are more vulnerable to malware attacks. Hackers can exploit known vulnerabilities in the software to gain access to the site and upload malware.
- Through weak passwords: If a website has weak or easily guessable passwords, it may be more vulnerable to malware attacks. Hackers can use tools to try to guess or “crack” passwords, and if they are successful, they may be able to upload malware to the site.
- Through phishing attacks: These are attacks that use email or other forms of communication to trick people into visiting a malicious website or downloading malware. For example, a hacker might send an email claiming to be from a reputable company and ask the recipient to click on a link to update their account information. If the recipient clicks on the link, they may be taken to a malicious website or download malware onto their computer.
- Through drive-by downloads: These are downloads that occur when a user visits a malicious website or clicks on a malicious link. The malware may be downloaded automatically, without the user’s knowledge or consent.
- Through SQL injection attacks: These are attacks that use vulnerabilities in a website’s database to inject malicious code into the site. Hackers can use this method to upload malware or to manipulate the website’s data.
- Through cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks: These are attacks that use vulnerabilities in a website to inject malicious code into the site. XSS attacks can be used to upload malware or to manipulate the website’s data.
It is important for website owners and operators to take steps to protect their sites from malware, such as keeping their software and servers up to date, using strong passwords, and implementing security measures like firewalls and antivirus software.

Malware Can Ruin Your E-commerce Business
Website malware can have serious consequences for online businesses, especially ecommerce websites. Some of the ways that malware can affect an online business include:
- Data theft: Malware can be used to steal sensitive data from an ecommerce website, such as customer names, addresses, and credit card information. This can lead to identity theft and financial losses for customers, as well as damage to the business’s reputation.
- Disruption of operations: Malware can disrupt the operation of an ecommerce website, making it unavailable to customers or causing errors and problems with orders and payments. This can lead to lost sales and revenue for the business.
- Damage to reputation: If an ecommerce website is infected with malware, it can damage the business’s reputation and make customers less likely to trust the site. This can lead to a loss of customers and revenue.
- Legal and compliance issues: If customer data is stolen or compromised as a result of malware on an ecommerce website, the business may face legal and compliance issues, such as fines and penalties.
It is important for online businesses, especially ecommerce websites, to take steps to protect their sites from malware. This can include keeping software and servers up to date, using strong passwords, and implementing security measures like firewalls and antivirus software.

How do I know if my website has malware?
There are several ways to check if your website has malware:
- Use a malware scanning tool: There are many tools available that can scan your website for malware. These tools work by analyzing the code and content of your website and looking for signs of malware. Some popular options include:
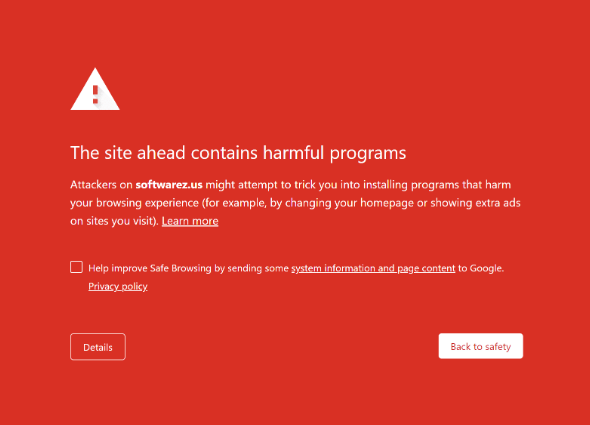
- Google Safe Browsing: This is a service provided by Google that checks websites for malware and other security issues. You can check your website using the Google Search Console.
- Sucuri: This is a website security company that offers a free malware scanner tool.
- Norton Safe Web: This is a service provided by Symantec that checks websites for malware and other security issues.
- Check your website logs: Your website logs can provide valuable information about any suspicious activity on your site. If you see any unusual requests or activity in your logs, it could be a sign of malware.
- Monitor your website traffic: If you notice a sudden drop in traffic or an increase in traffic from unfamiliar sources, it could be a sign that your website has been compromised.
- Check your website’s ranking: If your website’s ranking in search engine results suddenly drops, it could be a sign that your site has been infected with malware.
- Check with your hosting provider: Your hosting provider may have tools or services that can help you detect and remove malware from your website.
If you suspect that your website has been infected with malware, it is important to take immediate action to identify and remove the malware to prevent further damage to your site and your business.

How do you prevent website malware attack?
There are several steps you can take to prevent website malware attacks:
- Keep your software and servers up to date: Make sure that you are using the latest versions of all software and operating systems on your website and server. This can help to protect against known vulnerabilities that hackers might exploit.
- Use strong passwords: Use complex, unique passwords for all accounts related to your website, and make sure to change them regularly. Avoid using the same password for multiple accounts.
- Implement security measures: Use firewalls, antivirus software, and other security measures to protect your website and server. Regularly scan your site for vulnerabilities and take steps to fix any issues that are found.
- Educate your team: Make sure that your team is aware of the risks of malware and knows how to identify and prevent attacks.
- Monitor your website: Regularly check your website logs, traffic, and rankings to look for signs of malware.
- Use a web application firewall (WAF): A WAF is a security tool that monitors and protects your website from malicious traffic. It can help to block attacks and prevent malware from being uploaded to your site.
By taking these precautions, you can help to protect your website from malware attacks and keep it secure for your customers and users.